Banach limit
In mathematical analysis, a Banach limit is a continuous linear functional 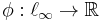 defined on the Banach space
defined on the Banach space 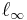 of all bounded complex-valued sequences such that for any sequences
of all bounded complex-valued sequences such that for any sequences 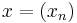 and
and 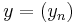 , the following conditions are satisfied:
, the following conditions are satisfied:
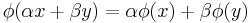 (linearity);
(linearity);- if
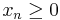 for all
for all 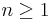 , then
, then 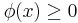 ;
; 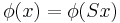 , where
, where 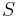 is the shift operator defined by
is the shift operator defined by 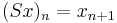 .
.- If
 is a convergent sequence, then
is a convergent sequence, then 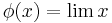 . Hence,
. Hence,
 is an extension of the continuous functional
is an extension of the continuous functional 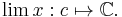
In other words, a Banach limit extends the usual limits, is shift-invariant and positive. However, there exist sequences for which the values of two Banach limits do not agree. We say that the Banach limit is not uniquely determined in this case. However, as a consequence of the above properties, a Banach limit also satisfies:
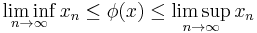
The existence of Banach limits is usually proved using the Hahn–Banach theorem (analyst's approach) or using ultrafilters (this approach is more frequent in set-theoretical expositions). It is worth mentioning, that these proofs use the Axiom of choice (so called non-effective proof).
Almost convergence
There are non-convergent sequences which have uniquely determined Banach limits. For example, if 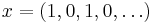 , then
, then 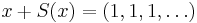 is a constant sequence, and
is a constant sequence, and 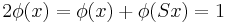 holds. Thus for any Banach limit this sequence has limit
holds. Thus for any Banach limit this sequence has limit 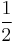 .
.
A sequence  with the property, that for every Banach limit
with the property, that for every Banach limit  the value
the value 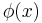 is the same, is called almost convergent.
is the same, is called almost convergent.
Ba spaces
Given a sequence in c, the ordinary limit of the sequence does not arise from an element of 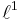 . Thus the Banach limit on
. Thus the Banach limit on 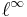 is an example of an element of the continuous dual space
is an example of an element of the continuous dual space 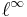 which is not in
which is not in 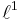 . The dual of
. The dual of 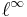 is known as the ba space, and consists of all finitely additive measures on the sigma-algebra of all subsets of the natural numbers.
is known as the ba space, and consists of all finitely additive measures on the sigma-algebra of all subsets of the natural numbers.